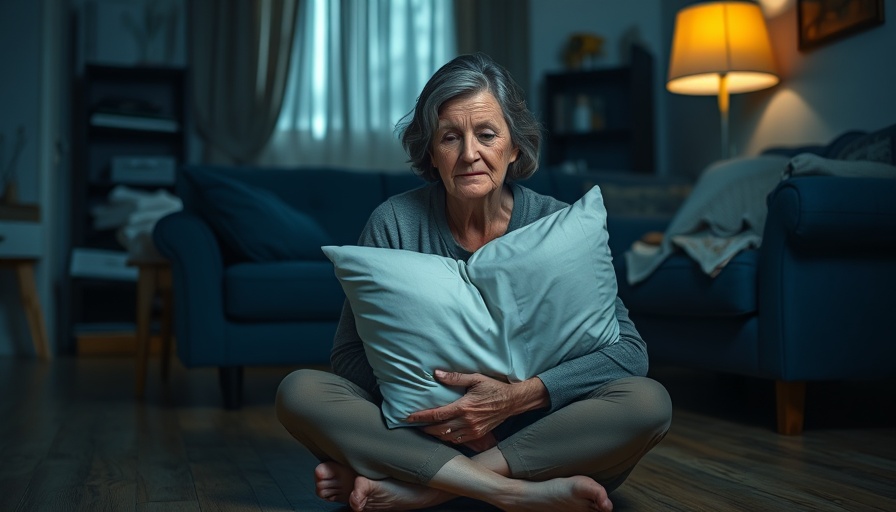

Why Loneliness Among Middle-Aged Adults is a Growing Concern
While many associate loneliness predominantly with older age groups, new research shows that middle-aged individuals in the U.S. are experiencing significant levels of loneliness. A recent study published in the journal Aging and Mental Health reveals that loneliness is more prevalent among those in their 50s and early 60s than among seniors. This startling finding shifts the narrative around the loneliness epidemic, often thought to be primarily a concern for older adults as they face increasing social isolation.
Reassessing the Loneliness Epidemic
Lead researcher Robin Richardson and her team analyzed data from over 64,000 individuals across 29 countries, finding a trend that bands together loneliness and life stages. Though generally, loneliness wanes with age in many cultures, the U.S. stands out as an exception. Middle-aged adults are reportedly grappling more with feelings of loneliness, making them a crucial group for targeted interventions.
The Impact of Societal Pressures
Research indicates that middle-aged individuals may struggle to socialize due to extensive responsibilities—from managing careers to caring for children and aging parents. The pressure of balancing these roles cuts into their leisure time, diminishing opportunities to connect with others. In fact, lack of employment was identified as a primary factor contributing to increased loneliness in this age demographic. However, the study revealed that nearly 20% of reported loneliness could not be attributed to identified factors, hinting at deeper societal issues at play.
Future Directions for Addressing Loneliness
Senior researcher Esteban Calvo highlighted the need for countries to develop nuanced approaches to combat this pressing issue. Investments in mental health screenings and support systems tailored to the specific needs of middle-aged adults—but often neglected—could lead to proactive solutions. Extending support to those who are unmarried or unemployed may play an essential role in mitigating loneliness across this vulnerable age group.
Why It Matters
Understanding the unique factors contributing to loneliness among middle-aged individuals can equip healthcare providers and policymakers with the tools to address these challenges effectively. As loneliness leads to numerous health risks, ranging from psychological disorders to increased mortality rates, refining our focus can have profound implications for societal well-being.
As public discourse evolves around health and community, recognizing the significance of emotional well-being for middle-aged populations becomes increasingly essential. Those affected should also feel empowered to seek support and resources available to them.
To learn more about how these issues intertwine and how you can protect your health, contact us for more details. Investing time in understanding and addressing loneliness can safeguard not just individual health, but community health overall.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment