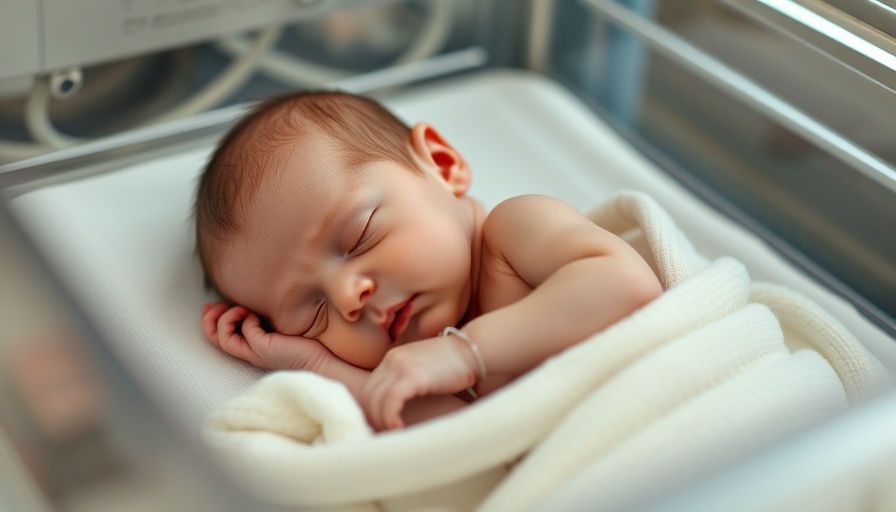

AI Transforms Nutrition for Premature Infants
In the realm of neonatal care, artificial intelligence (AI) is making significant strides in improving the feeding regimens of premature infants, commonly referred to as preemies. A recent study found that AI can enhance Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN), offering a vital solution for the nearly 10% of babies born prematurely, who require IV feeding when their digestive systems are not prepared to process nutrients.
The Challenges of Current TPN Practices
Traditionally, healthcare professionals have faced numerous challenges when prescribing individualized TPN for preemies. Each day, prescriptions are crafted from scratch, a labor-intensive process fraught with potential errors. According to senior researcher Nima Aghaeepour from Stanford University, TPN represents the largest source of medical error in neonatal units, with the absence of reliable blood tests to diagnose whether an infant’s nutritional needs are being met contributing to these challenges.
How AI Makes a Difference
To tackle this issue, researchers developed an AI program trained on approximately 80,000 past TPN prescriptions combined with patient outcomes. This AI system utilizes electronic medical data to predict the specific nutrient needs of individual preemies, thereby streamlining the IV nutrition process. Impressively, in tests, the AI's recommendations outperformed those made by human doctors.
Standardizing Care With AI
The researchers narrowed down the extensive variability of TPN prescriptions to just 15 standard formulas, which still closely align with what experienced medical professionals would have prescribed. This simplified approach not only increases the safety and speed of delivering nutrition but significantly reduces the potential for human error.
Proven Results in Nutritional Outcomes
In trials where medical professionals evaluated the effectiveness of AI-generated prescriptions against traditional methods, the AI recommendations were consistently favored. Moreover, when examining past cases, it became evident that deviations from AI-prescribed nutrition correlated with increased risks of severe complications, such as necrotizing enterocolitis and potential mortality.
The integration of AI-driven nutritional guidelines could provide immeasurable benefits to the fragile lives of preemies, contributing to healthier development outcomes. Knowing that the nutritional foundation is being handled with precision may offer comfort to caregivers and families navigating the stress of neonatal care.
As the healthcare industry continues to embrace AI technologies, the revolutionary adjustments in how we approach the nutrition of our most vulnerable infants signify hope and progress in pediatric medicine. For more insights into this exciting development and its impacts on neonatal care, contact us for more details.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment