In a world where one-size-fits-all solutions often fall short, the compounding pharmacist emerges as a vital ally in your healthcare journey . Titled “Unlock Solutions: How the Compounding Pharmacist Can Transform Your Health,” this article dives into the fascinating realm of personalized medicine, showcasing how these specialists can address unique health challenges with tailored therapies. By understanding their role as problem-solving experts, you’ll discover how to enhance your health outcomes and reclaim control over your wellness. Let’s unlock the potential together!
Understanding the Role of the Compounding Pharmacist
The compounding pharmacist is the problem solving specialist who plays an integral role in the healthcare team. Unlike traditional pharmacists who dispense ready-made medications, compounding pharmacists create customized medications tailored to individual patient needs. This flexibility allows them to formulate drugs in various dosage forms, such as creams, capsules, or liquids, to meet specific health requirements.
Key Responsibilities of Compounding Pharmacists:
- Preparation of Customized Medications : They prepare medications based on prescriptions from healthcare providers.
- Consultation : They discuss medication options and dosages with patients and healthcare professionals.
- Quality Control : They ensure that all compounded medications meet safety and quality standards.
Comparison of Traditional vs. Compounding Pharmacists
Feature |
Traditional Pharmacist |
Compounding Pharmacist |
|---|---|---|
Prepares ready-made medications |
Yes |
No |
Customizes medications |
No |
Yes |
Consultation |
Limited |
Extensive |
Dosage forms |
Standardized only |
Customized based on patient needs |

“Compounding pharmacists are not just dispensers; they are problem solvers who tailor solutions for each patient.”
Career Path of a Compounding Pharmacist
To become the compounding pharmacist is the problem solving specialist , one must navigate a specific career path that includes extensive education and training. Most pharmacists start by earning a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) degree, followed by specialized training in compounding.
Pharmacy Specialties and the Compounding Pharmacist
The career of a compounding pharmacist often branches into various specialties, including:
Sterile Compounding : Preparing medications that require sterile conditions.
Pediatric Compounding : Formulating medications for children, often in liquid form or flavored options.
Dermatological Compounding : Creating skin medications like creams and gels.
Steps to Become a Compounding Pharmacist
Complete a Pharmacy Degree : Enroll in an accredited pharmacy school and obtain a Pharm.D.
Gain Experience : Work in a pharmacy setting to understand daily operations.
Board Certification : Consider obtaining board certification in pharmacy specialties to enhance your expertise.

“Education and hands-on experience are crucial for anyone looking to specialize in compounding pharmacy.”
Personalized Medicine: The Cornerstone of Compounding
At the heart of the compounding pharmacist is the problem solving specialist is the concept of personalized medicine. This approach tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, making it one of the most effective strategies in modern healthcare.
How Compounding Pharmacists Create Customized Medications
Compounding pharmacists can create tailored medications that address unique patient needs, such as:
Adjusting Dosages : For patients who require lower or higher doses than commercially available drugs.
Eliminating Allergens : Formulations can exclude specific allergens like gluten or lactose.
Creating Unique Dosage Forms : Such as transdermal gels for easier application.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine :
- Improved adherence to medication regimens.
- Enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
- Reduced side effects due to customized formulations.

Compounding Services and Dosage Forms
Compounding pharmacists offer a variety of services and dosage forms that are crucial for modern patient care. Understanding these options can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Side Effects and Safety in Compounded Medications
While compounded medications can offer many benefits, they also come with potential side effects. It is vital for pharmacists to inform patients about these risks:
Common Side Effects : Allergic reactions, local irritation, and gastrointestinal issues.
Safety Precautions : Compounding pharmacies must adhere to strict regulatory standards set by the board of pharmacy to ensure safety.
Common Dosage Forms in Compounding :
| Dosage Form | Example Applications |
|----------------------|----------------------------------------------|
| Topical creams | Skin conditions |
| Capsules | Customized dosages |
| Liquid preparations | Pediatric patients needing flavored options |
“Safety is paramount in compounding, and pharmacists must stay vigilant in adhering to established guidelines and standards.”
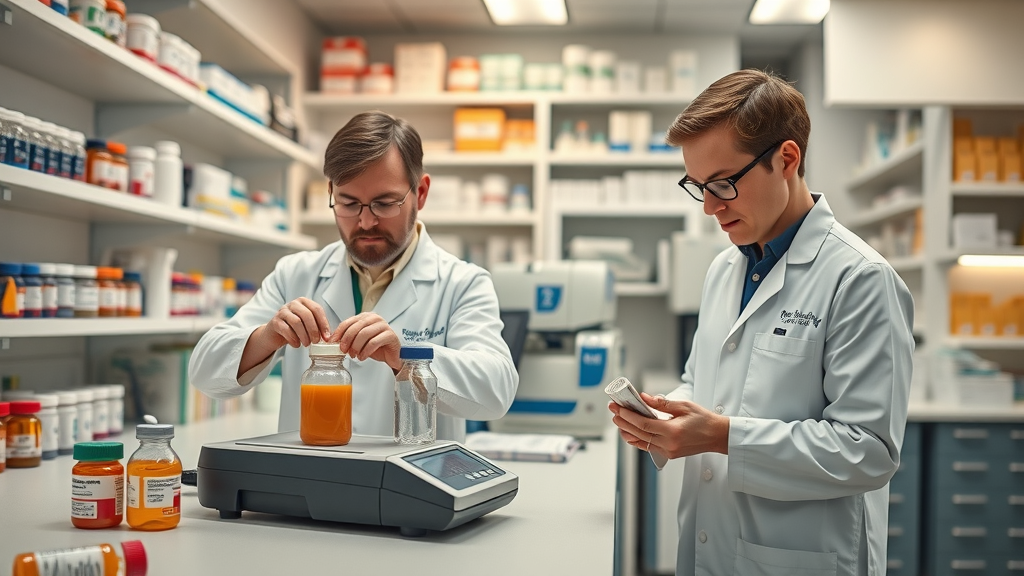
The Compounding Center: Innovation and Standards
The compounding center is where the magic happens. Innovation and adherence to strict manufacturing processes are crucial for ensuring that compounded medications are safe and effective.
Adhering to Manufacturing Processes and Standards
Compounding pharmacists must comply with regulations set by various authorities, including the Board of Pharmacy and the International Academy of Compounding Pharmacists . These standards ensure that all compounded medications are prepared with the utmost care and precision.
Key Practices in Compounding Centers :
- Quality Assurance : Regular testing of compounded products.
- Training and Certification : Continuous education for pharmacists to stay updated on best practices.
- Sterile Compounding Techniques : Following protocols to prevent contamination.

The Future of Compounding Pharmacy
As healthcare continues to evolve, the role of the compounding pharmacist is becoming more critical. They are not only the problem-solving specialists but also innovators in personalized medicine.
Challenges Faced by Compounding Pharmacists
Despite their importance, compounding pharmacists face several challenges:
Regulatory Changes : Keeping up with new regulations can be difficult.
Public Awareness : Many patients are unaware of the benefits of compounded medications.
Technological Advancements : Adapting to new technologies can require ongoing training.

Key Takeaways: The Compounding Pharmacist’s Role in Healthcare
In summary, the compounding pharmacist is the problem solving specialist who plays a vital role in modern healthcare. Their ability to create customized medications that cater to individual patient needs makes them indispensable members of the healthcare team.
Key Takeaways :
- Compounding pharmacists provide tailored solutions for unique health challenges.
- Their expertise is essential for personalized medicine.
- Compliance with safety and quality standards is critical in compounding pharmacies.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a traditional pharmacist and a compounding pharmacist?
- Traditional pharmacists dispense pre-manufactured medications, while compounding pharmacists create customized formulations tailored to individual patient needs.What qualifications are necessary to become a compounding pharmacist?
- A Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) degree, followed by specialized training and possibly board certification in compounding.Are compounded medications safe?
- Yes, when prepared in licensed compounding pharmacies that adhere to regulations and quality standards.
In conclusion, the role of the compounding pharmacist as the problem solving specialist cannot be overstated. By creating personalized medications, they are transforming healthcare one patient at a time.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment