Are you one of the millions grappling with high cholesterol ? You’re not alone, and the good news is that you have the power to change your health for the better! In our article, we delve into the critical importance of managing your daily routine to improve your cholesterol levels, highlighting actionable tips so you can make lifestyle changes that will improve and boost your heart health. Don’t wait until it’s too late—join us in uncovering these essential strategies for a healthier, happier you!
What is High Cholesterol?
High cholesterol is a condition characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, causing fatty deposits which can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and stroke. Cholesterol is a waxy substance that your body needs to build cells and produce certain hormones. However, too much cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, narrowing them and affecting blood flow.
Types of Cholesterol
Cholesterol travels through your bloodstream in different forms called lipoproteins. The main types include:
Type of Cholesterol |
Description |
Impact on Health |
|---|---|---|
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) |
Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol as it contributes to plaque buildup in arteries. |
Increased risk of heart disease and stroke. |
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) |
Known as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. |
Protects against heart disease. |
Triglycerides |
A type of fat found in the blood; high levels can increase heart disease risk. |
Linked to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. |
HDL and LDL Levels
Maintaining a healthy balance between HDL and LDL levels is crucial for cardiovascular health. Ideally, you want high levels of HDL and low levels of LDL.
The Role of Triglycerides
Triglycerides are another important factor in your cholesterol profile. High triglyceride levels, often associated with high cholesterol, are a significant risk factor for health problems as well as heart disease.
Risk Factors Associated with High Cholesterol
Understanding the risk factors associated with high cholesterol can help you manage and potentially lower your levels. Various factors contribute to the risk of high cholesterol including age, genetics, and lifestyle.
Age and Gender Influences
As you age, your cholesterol levels can naturally increase. Men typically experience higher cholesterol levels at a younger age compared to women, who may see an increase after menopause.
Genetics and Family History
Genetics play a critical role in your cholesterol levels. Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disorder that results in high cholesterol levels, increasing heart disease risk at a young age.
Lifestyle Factors
Your daily habits significantly impact your cholesterol levels. It is important to stay away from an unhealthy lifestyle. Here are some lifestyle factors to consider:
Dietary Choices and Trans Fats
Avoid trans fats: Found in many processed foods, trans fats can increase LDL levels and lower HDL levels.
Limit saturated fats: Found in red meat and full-fat dairy products, they can raise total cholesterol levels.
Physical Activity Levels
Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity can help raise HDL levels and lower LDL levels.
Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise can lead to weight gain, which is linked to higher cholesterol levels.

Health Implications of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can lead to several serious health conditions, such as coronary artery disease. Understanding these implications is crucial for managing your health.
Heart Disease and Stroke Risks
High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Elevated LDL levels can lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, which can ultimately result in blockages.
Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) occurs when narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. This condition can cause pain and mobility issues.
Understanding Plaque Buildup
Plaque buildup in arteries is often silent until significant damage has occurred. Regular monitoring is essential to detect potential problems early and protect the walls of your arteries.
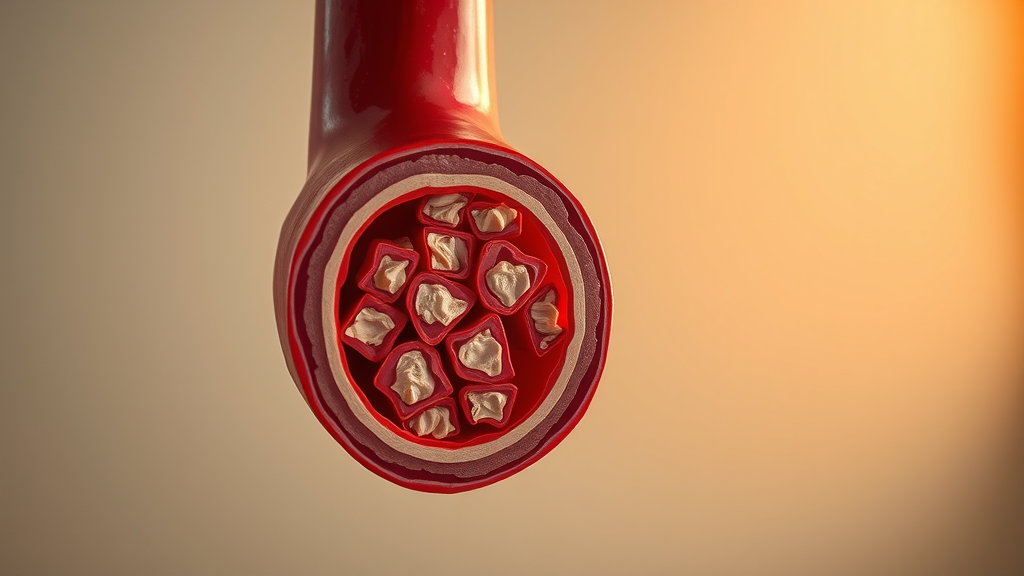

How to Manage High Cholesterol
Managing high cholesterol involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medications. Here’s how you can take control of your health.
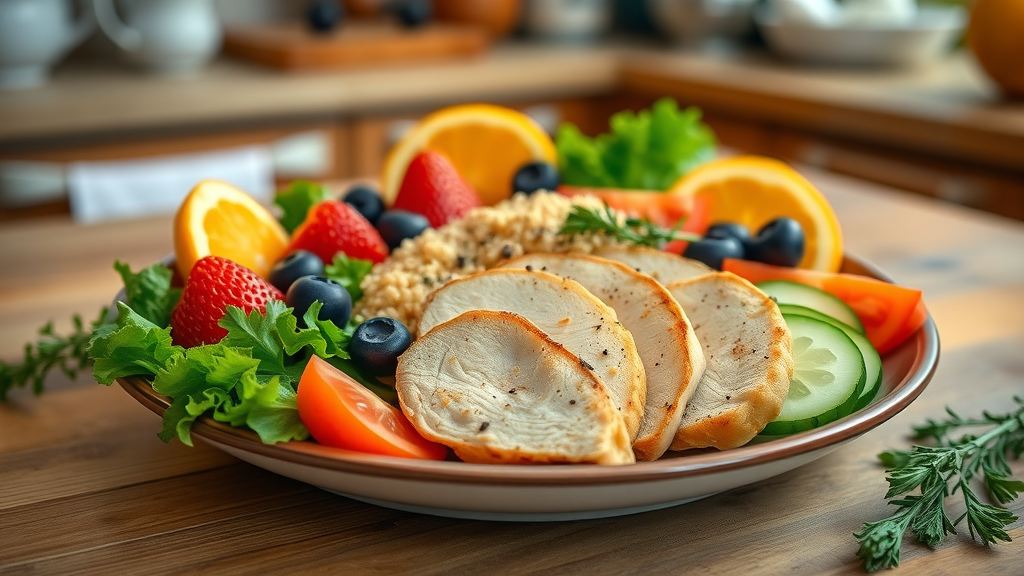
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy Eating Habits
Opt for healthy fats: Include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in olive oil and avocados.
Increase fiber intake: Foods high in soluble fiber, like oats and beans, can help lower cholesterol levels.
Regular Exercise Routines
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. Exercise not only helps lower cholesterol but also improves overall cardiovascular health.

Medications for High Cholesterol
When lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medications may be necessary. Consult with your healthcare provider about options.
Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
Statins: Commonly prescribed to lower LDL levels.
Bile acid sequestrants: Help lower cholesterol levels by binding bile acids.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Regular check-ups are essential. Talk with your provider if you notice symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath.

Regular Testing and Monitoring
Regular testing is crucial for managing high cholesterol effectively.
Importance of Blood Tests
Blood tests help determine your cholesterol levels and overall lipid profile, guiding your management plan.
Frequency of Cholesterol Tests
Annual screenings: Recommended for adults starting at age 20.
More frequent tests: May be necessary if you have risk factors or a family history of high cholesterol.
Interpreting Test Results
Understanding your cholesterol numbers is vital. Here’s a quick reference:
Cholesterol Level |
Interpretation |
|---|---|
Total Cholesterol < 200 mg/dL |
Desirable |
Total Cholesterol 200-239 mg/dL |
Borderline high |
Total Cholesterol ≥ 240 mg/dL |
High |

Innovative Tools and Apps for Managing Cholesterol
Technology can play a key role in managing high cholesterol effectively.
The Mayo Clinic App
Use the Mayo Clinic App to track your health progress, including cholesterol levels.
Tracking Your Health Progress
Record your meals: Helps monitor dietary choices affecting cholesterol.
Exercise log: Keep track of physical activity and its impact on cholesterol.
Using Digital Resources Effectively
Explore online resources and tools that can help you stay informed about managing cholesterol.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
Managing high cholesterol is essential for preventing serious health conditions. Here are the key takeaways:
Know your cholesterol numbers: Regular testing is crucial for management.
Adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle: Focus on healthy eating and regular exercise.
Consult your healthcare provider: Discuss medication options if lifestyle changes aren’t enough.
Stay informed: Utilize apps and online resources to track your health.
Monitor your risk factors: Family history and age can influence your cholesterol levels.

Call us at 984-238-6164 and check our website https://MyWellnessTrain.com/Network
By understanding high cholesterol and implementing these actionable strategies, you can take control of your health and significantly lower your risk of heart disease and other related conditions. Don’t wait—start making changes today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is considered a high cholesterol level?
A: Total cholesterol levels above 240 mg/dL are considered high.
Q: Can diet alone lower cholesterol?
A: Yes, a heart-healthy diet can significantly lower cholesterol levels when combined with lifestyle changes.
Q: How often should I get my cholesterol checked?
A: Adults should have cholesterol tests every 4-6 years, and more frequently if they have risk factors.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment